Lesson 1.3: Why STEAM Matters in the 21st Century
The Challenges of the 21st Century World
The 21st-century world faces increasingly complex, multidimensional, and dynamic global challenges. Climate change, the rapid acceleration of technology, job automation, and the emergence of disruptive technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain all require cross-disciplinary approaches to find solutions (Yuliani, 2021). The world can no longer be understood within narrow academic boundaries. What is needed is a systemic, holistic, and flexible way of thinking that integrates diverse perspectives.
The STEAM approach emerges as a response to this need. STEAM encourages learners to develop adaptive, creative, and transformative competencies that are crucial for navigating an uncertain and fast-changing world (Nasution & Simatupang, 2020). Recent research by Fauzi et al. (2021) shows that the implementation of STEAM significantly enhances students’ problem-solving abilities and technological literacy at the primary education level.
Furthermore, an increasingly interconnected world also demands that individuals understand global issues such as sustainability, technology ethics, and social justice. STEAM enables students to build sensitivity toward these issues through integrative and applied learning.
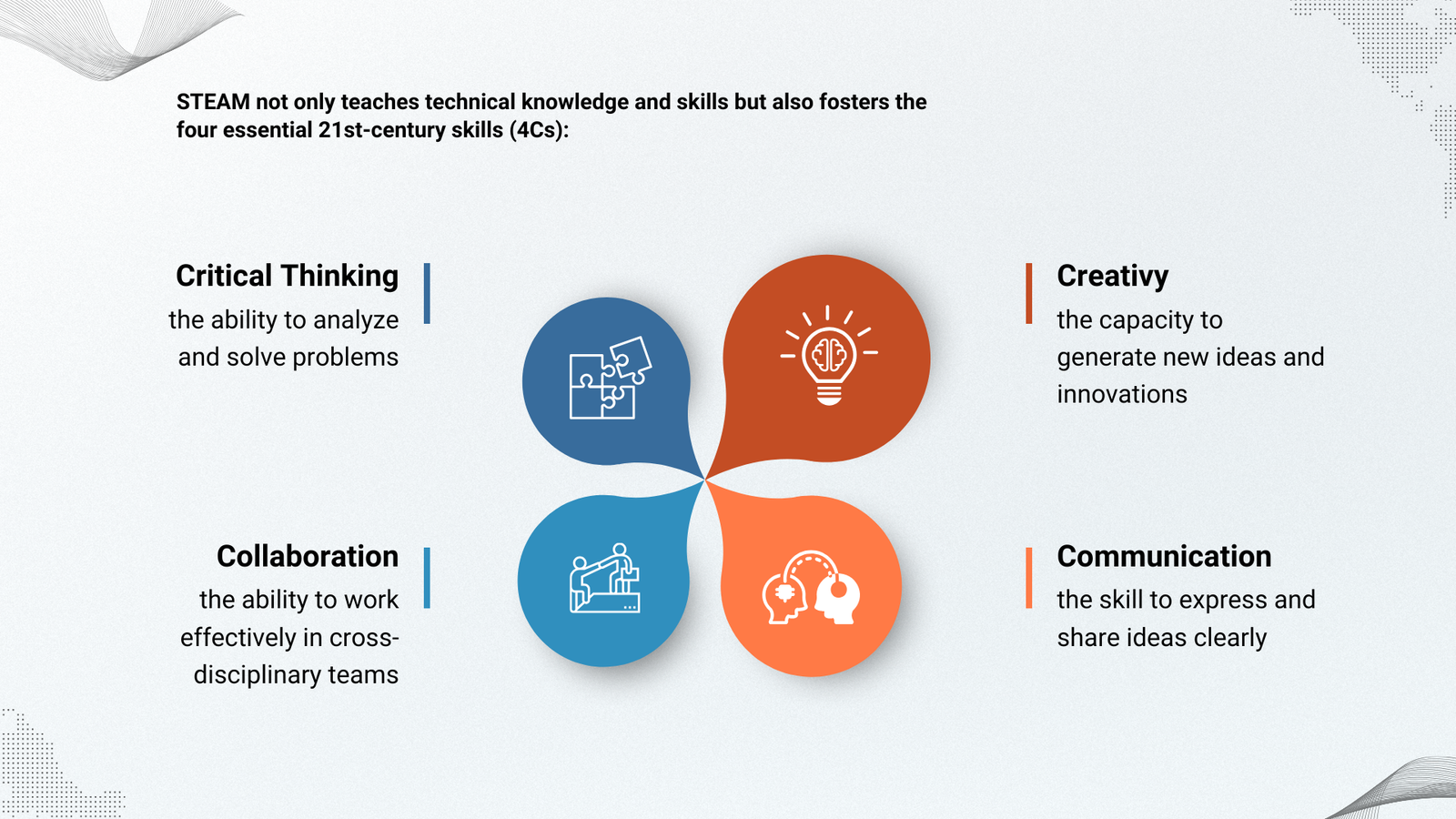
The 21st-century skill set, known as the 4Cs: Critical Thinking, Creativity, Communication, and Collaboration has become an urgent need in today’s education (Trilling & Fadel, 2018). STEAM naturally facilitates the development of these skills through Project-Based Learning and Authentic Learning approaches.
Through STEAM, students are guided to:
- Critical Thinking: Analyze diverse information from various sources and make data-driven decisions.
- Creativity: Generate original and innovative ideas to solve problems.
- Communication: Effectively convey ideas both verbally and visually.
- Collaboration: Work in teams across different interests and backgrounds.
Moreover, the integration of STEAM also fosters digital literacy, computational thinking, and mental resilience (Dewi & Wahyuni, 2021; Kartika & Permana, 2022). These abilities equip students to face an increasingly complex and uncertain future with greater readiness.
The Role of STEAM in Shaping the Future
STEAM plays a crucial role in shaping a generation of innovators, social entrepreneurs, and future leaders. Through STEAM, students do not merely learn to create functional products or solutions, but also learn to prioritize values such as sustainability, aesthetics, and social impact.
Fitriani and Nugroho (2022) emphasize that the STEAM approach encourages empathy-based learning that focuses on human needs. This concept aligns with the principles of Design Thinking, which is widely adopted in the creative and technology industries today.
Research by Putri et al. (2023) shows that STEAM-based learning is effective in enhancing students’ innovation and social entrepreneurship skills at the secondary education level, especially when linked to environmental issues and sustainable development.
The Fourth and Fifth Industrial Revolutions have created new demands in the world of work, requiring a combination of skills that blend technology, the arts, and the humanities. Future professions such as augmented reality designers, renewable energy developers, data visualization analysts, and smart city architects increasingly demand graduates capable of cross-disciplinary thinking and innovation.
Indriani & Huda (2020) demonstrate that graduates with a STEAM background tend to adapt more easily to emerging fields that are technology- and creativity-driven. Moreover, research by Syahputra et al. (2022) found that STEAM-based learning improves students’ readiness to enter the global workforce by fostering complex competencies such as problem-solving, virtual collaboration, and social intelligence.
STEAM also fosters the emergence of technology and social entrepreneurs capable of creating new job opportunities based on creative and innovative ideas.
Case Study: STEAM Figures and Projects
World figures such as Elon Musk, Steve Jobs, and Tim Berners-Lee are real examples of the application of STEAM principles in creating innovations that have transformed the world. They are not merely scientists or technologists, but visionaries who have been able to combine creativity, technology, and human needs.
At the educational level, a case study conducted at a secondary school in Bandung showed that a STEAM project involving the creation of a water filtration device made from local materials not only enhanced students’ science and engineering competencies but also increased their social awareness and visual communication skills (Rohmah et al., 2022).
Another example is the “Eco-STEM” program developed in several schools in Yogyakarta, where students are involved in designing simple tools based on renewable energy while also considering local aesthetic and socio-cultural aspects (Hapsari & Kurniawan, 2021).
These projects demonstrate that STEAM is not solely about technology it is also about building empathy, sustainability, and social sensitivity.
References
Dewi, R., & Wahyuni, S. (2021). Penguatan keterampilan abad 21 melalui pendekatan STEAM di sekolah dasar. Jurnal Basicedu, 5(6), 5990–5998. https://doi.org/10.31004/basicedu.v5i6.1699
Fauzi, A., Santika, R., & Mulyani, S. (2021). Penerapan model pembelajaran berbasis STEAM untuk meningkatkan kemampuan problem solving siswa. Jurnal Pendidikan Sains Indonesia, 9(4), 512–520.
Fitriani, N., & Nugroho, S. (2022). STEAM sebagai pendekatan pembelajaran inovatif berbasis kewirausahaan sosial. Jurnal Pendidikan dan Teknologi Indonesia, 2(1), 33–42.
Hapsari, R. P., & Kurniawan, D. (2021). Implementasi Eco-STEM dalam meningkatkan keterampilan abad 21. Jurnal Pendidikan MIPA, 21(1), 15–22.
Indriani, Y., & Huda, M. (2020). Peran pendidikan STEAM dalam menyiapkan lulusan menghadapi tantangan revolusi industri 4.0. Jurnal Pendidikan Vokasi, 10(1), 88–96.
Kartika, R., & Permana, R. (2022). STEAM education dalam meningkatkan literasi digital siswa sekolah menengah. Jurnal Pendidikan Sains dan Humaniora, 7(2), 123–131.
Nasution, M. K., & Simatupang, M. (2020). STEAM education untuk pengembangan keterampilan abad 21 pada siswa. Jurnal Inovasi Pendidikan, 4(3), 145–152.
Putri, D. A., Subekti, S., & Ardianti, N. (2023). STEAM project-based learning untuk meningkatkan inovasi dan kewirausahaan sosial. Jurnal Pendidikan Sains, 11(1), 25–32.
Rohmah, K., Suprapto, N., & Zulaikha, S. (2022). Implementasi STEAM dalam pembelajaran sains berbasis proyek: Studi kasus pengembangan alat penyaring air. Jurnal Inovasi Pendidikan IPA, 8(1), 11–20.
Syahputra, E., Hidayat, R., & Pratama, A. (2022). Penguatan soft skills berbasis STEAM untuk kesiapan kerja generasi milenial. Jurnal Pendidikan Teknologi dan Kejuruan, 19(2), 150–160.
Trilling, B., & Fadel, C. (2018). 21st Century Skills: Learning for Life in Our Times. Jossey-Bass.
Yuliani, S. (2021). Pendidikan berbasis STEAM untuk menghadapi tantangan revolusi industri 4.0. Jurnal Ilmiah Pendidikan, 9(2), 34–45.
